The Urinogenital System
Male Reproductive System
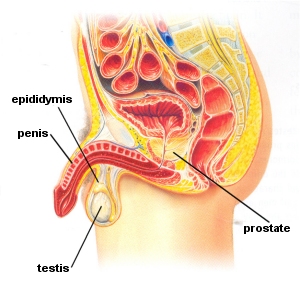
In the male, the pevlic girdle protects the internal organs of the reproductive system, the bladder and the rectum. The male has external genitals comprised of the scrotum - which holds the testes - and the penis.
Penis
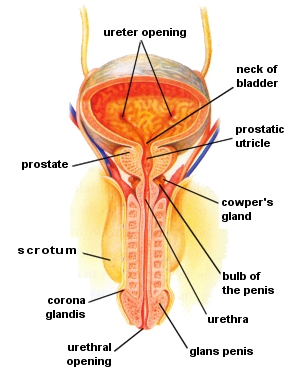
The penis is the main external sex organ in the male and has three main parts:
- erectile tissue - filled with blood vessels, the penis becomes erect and enlarged when blood flow to the tissue increases, eventually making the penis rigid allowing penetration of the female's vagina and thus ensuring delivery of semen.
- foreskin - a loose double fold of skin surrounding the glans and thus protecting them.
- urethra - the duct for both urine and semen.
Prostate
The prostate gland is situated between the bladder and the rectum and surrounds the begining of the urethra.
The prostate produces two secretions - one to maintain the moisture in the lining of the urethra and the other to aid the passage of sperm through the urethra and inside the uterus.
Testes
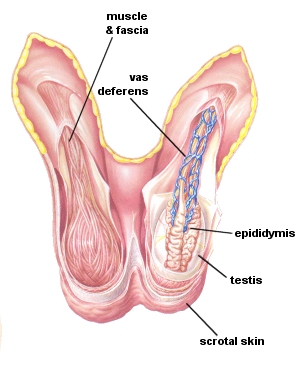
The testes (singular testis or testicle) and the male gonads contained within the scrotum. They produce spermatozoa and testosterone and because the testes are outside the body, the temperature of maturing sperm can be regulated so that they remain slightly cooler than body temperature.
Epididymis
The epididymis is a tightly coiled tube, opening from each testis, down along the side of the gland and straight into the vas deferens. It stores and transports sperm and provides a place for immature sperm to develop.
Vas Deferens
The vas deferens are ducts that have muscular walls, leading from the epididymis to the urethra. They act as a passageway for the transfer of sperm from the storage area (epididymis) to the prostatic urethra and ultimately the penis. The muscular walls allow for contractions to move sperm along the duct.
Sperm consists of a head (the male sex cell), a middle section anda tail to propel the sperm along the vagina and into the uterus.
The head is a nucleus that contains the 23 chromosomes. The sperm fertilise ova produced by the female and the head inserts itself into the ovum so that mitosis can begin.